Fiber-Based PS-OCT for Endoscopic Neuro Access
- Degree programme: BSc in Mikro- und Medizintechnik
- Author: Lukas Tschabold
- Thesis advisors: Dr. Dominik Inniger, Philipp Scheich
- Expert: Matthew Lapinski
- Industrial partner: Clee Medical SA Geneva
- Year: 2025
Brain tumor biopsies are often performed without real-time image guidance, which increases the risk of complications such as inaccurate positioning. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) provides high-resolution, depth-resolved images. Polarization-Sensitive OCT (PS-OCT) adds the ability to detect subtle tissue changes. This thesis focuses on designing, constructing, and evaluating a PS-OCT system.
Context
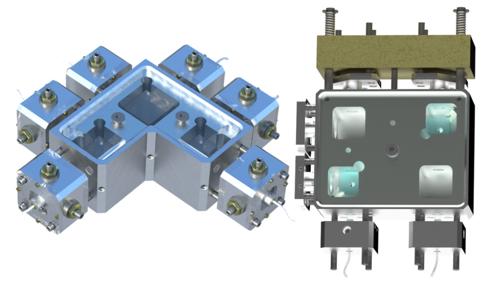
The PS-OCT system uses a 1310 nm swept-source laser and a fiber-based interferometer. Light passes through the Polarization Delay Unit (PDU), reflects off tissue, and is captured by the PS-Balanced Detection Unit (PS-BDU), enabling depth-resolved, polarization-sensitive imaging.
Methods
This thesis focuses on the development of the two key components: 1) The PDU, which splits light into orthogonal polarization states and introduces a spatial offset. A redesigned structure improves alignment, mechanical stability, and delay control. This allows for precise phase shift between the two states. 2) The PS-BDU, which superposes incoming light and uses balanced detection to record the polarization-encoded signal. The newly developed unit achieves 72–82% coupling efficiency.
Results
The PS-OCT system demonstrates excellent sensitivity of 107 dB and is ready to be tested with an endoscopic probe in brain tissue.